Below is a preview of the main elements you will use to describe each of these concepts. Each plot has one value in percent for canopy cover.

Frequency Distribution Quick Introduction
I have a question about the correct distribution to use for creating a model with my data.

. From looking at the histogram we can get only a rough estimate for the center of the distribution. Means are used to describe variables that are normally distributed. Center shape spread and outliers.
And it may not give you the. The sum of all probabilities for all possible values must equal 1. It is a prerequisite for both the various graphs used to display data and the basic statistics used to describe a data set -- mean median mode variance standard.
The variability or dispersion concerns how spread out the values are. Take the lower-ranked value in step 3 and add the value from step 4 to obtain the interpolated value for. Understand how to examine the association between categorical variables by comparing conditional and marginal percentages.
S dfkeywords counts svalue_counts percent svalue_countsnormalizeTrue percent100 svalue_countsnormalizeTruemul100round1astypestr pdDataFramecounts. Where possible this report includes measures of data variability to describe the range of values that can be reasonably expected at any given site. Distribution fitting is the process used to select a statistical distribution that best fits a set of data.
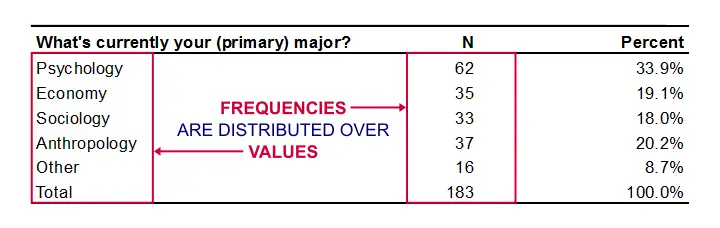
You can apply these to assess only one variable at a time in univariate analysis or to compare two or. Find the joint marginal and conditional distributions from a two-way table of the counts by hand and with SPSS. Count Percent Frequency Shows how often something occurs Use this when you want to show how often a response is given.
What is the marginal distribution for gender in percentages. For each plot I estimated the percentage of tree canopy that shades the ground. The PERCENT_RANK function calculates the percentage rank of each value in a partition relative to the other rows in the partition.
Measures of Central Tendency Mean Median and Mode Locates the distribution by various points Use this when you want to show how an average or most commonly indicated response. Marginal Distributions for Counts. Converting these raw numbers into percentages would then provide an even more useful description of the data.
The process of creating a percentage frequency distribution involves first identifying the total number of observations to be represented. In the following sections well explain each of these terms one by one. Furthermore the probability for a particular value or range of values must be between 0 and 1.
If you are faced with Measure and Scale that is the amount obtained from a variable in each group and now you want to compare the values then use the t test. The frequency distribution is the foundation of descriptive statistics. However we can describe a categorical distributions typical value with the mode and can also note its level of variability.
The marginal distribution for movie genre is. Then we are going to calculate the count and percent. Percentages range from 0 to 095.
Means and medians which are used to summarize continuous data and percentages which are used to summarize categorical data. There are 3 main types of descriptive statistics. The value_counts can be used to bin continuous data into discrete.
It works in the same way as RANK but rather than returning a rank as an integer it returns the percentage point at which a given value occurs in the ranking. Types of descriptive statistics. Take the difference between these two observations and multiply it by the fractional portion of the rank.
Value_counts percentage view dfcourse_difficultyvalue_countsnormalizeTrue value_counts as percentages 6 value_counts to bin continuous data into discrete intervals. Examples of statistical distributions include the normal Gamma Weibull and Smallest Extreme Value distributions. Percentage is calculated by taking the frequency in the category divided by the total number of participants and multiplying by 100.
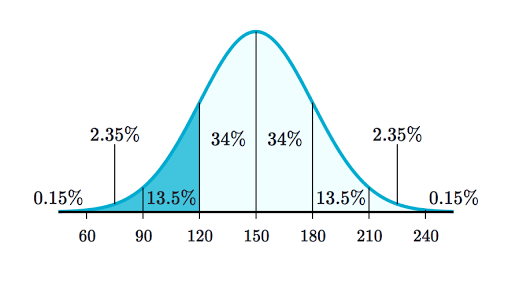
P x the likelihood that random variable takes a specific value of x. Here is an example of a normally distrbuted. An individual piece of count data is often termed a count variableWhen such a variable is treated as a random variable the Poisson binomial and negative binomial distributions are commonly used to represent its distribution.
In this way they describe the distribution of a categorical. This is one great hack that is commonly under-utilised. The central tendency concerns the averages of the values.
Measures of Dispersion or Variation. The distribution concerns the frequency of each value. Another common way to measure the center of a distribution is to use the average value.
Probability distributions describe the dispersion of the values of a random variable. In Table 3 if there were 100 participants in the study 55 would be female. Notice that to compute both of these percentages you need both total counts as well as the count of the number of women accounting majors.
The marginal distribution for gender is. More exact ways of finding measures of. Mean The mean or average is calcuated as the sum of values divided by the count of values.
Both types of tables show how the cases are distributed across the categories. Usually we multiply by 100 to express these proportions as percentages. If the answer is no then.
A relative frequency table Table 42 displays the percentages rather than the counts of the values in each category. To calculate the percentage of males in Table 3 take the frequency for males 80 divided by the total number in the sample 200. Then counting the total number of observations within each data point or grouping of data points.
For our example this is. Be able to recognize when a variable is categorical and choose an appropriate display for it. Many times percentage frequency distributions are displayed as tables or as bar graphs or pie charts.
And then dividing the number of. In the example above you are trying to determine the process capability of your non-normal process. I conducted a forest inventory with 50 plots each plot measures 20m 50m.
40 3504 2. Percentages are very convenient for comparisons but a table with only percentages in it does not give you as much information as a table with the actual counts. Determine from the wording of the story whether the question is asking for a joint marginal or conditional percentageprobability.
Considerably from these patterns. The Mode of a dataset is the most frequently occurring value. This is particularly true of the percentage of vehicles by vehicle category since some vehicle categories are not commonly found in some parts of the country.
Define and describe the features of the distribution of one quantitative variable shape center spread. The tables display counts frequencies and percentages or proportions relative frequencies. When describing distributions on the AP Statistics exam there are 4 key concepts that you need to touch on every time.
Be able to summarize the distribution of a categorical variable with a frequency table. There can be more than one mode in a data. Know when it two-way tables and the chi-square test are the correct statistical technique for a story.
Graphical examination of count data may be aided by the use of data transformations chosen to have the property of.
Frequency Distribution Quick Introduction

Chi Square Test Tests For Association Between Two Categorical Variables Chi Square Test Performs Two Types Of Functi Statistics Math Chi Square Research Skills

0 Comments